What is Modular Programming?
Modular programming is the process of breaking down a problem into smaller tasks. These tasks can then be broken down into sub-tasks.
Modular programming is an important and beneficial approach to programming problems.
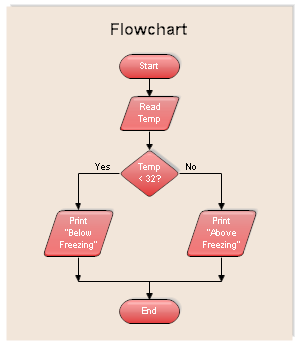
Example
Following diagram is showing how we can divide a task into sub-tasks.
Benefits of modular programming
Distributed development
Modular programming allows distributed development. By breaking down the problem into multiple tasks, different developers can work in parallel. And this will shorten the development time.
Code re-usability
A program modules can be reused in the programs. This is a convenient feature because it reduces redundant code. Modules can also be reused in future projects. It is much easier to reuse a module than recreate program logic from scratch.
Program readability
Modular programming leads to more readable programs. Modules can be implemented as user defined functions. A programs with a plenty of functions is straightforward. But a program with no functions can be very long and hard to follow.
Manageable task
Breaking down a programming project into modules makes it more manageable. These individual modules are easier to design, implement and test. Then you can use these modules to construct the overall program.